Amidst the ever-changing threat landscape, new tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) seem to emerge daily, creating extreme challenges for security teams. The broad range of attack methods utilized by attackers seems to present an insurmountable problem: how do you defend against a playbook that does not yet exist?
Faced with the growing number of novel and uncommon attack methods, it is essential for organizations to adopt a security solution able to detect threats based on their anomalies, rather than relying on threat intelligence alone.
In March 2023, Darktrace observed an emerging trend in the use of an application known as ‘PerfectData Software’ for probable malicious purposes in several Microsoft 365 account takeovers.
Using its anomaly-based detection, Darktrace DETECT™ was able to identify the activity chain surrounding the use of this application, potentially uncovering a novel piece of threat actor tradecraft in the process.
Microsoft 365 Intrusions
In recent years, Microsoft’s Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) suite, Microsoft 365, along with its built-in identity and access management (IAM) service, Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), have been heavily targeted by threat actors due to their near-ubiquitous usage across industries. Four out of every five Fortune 500 companies, for example, use Microsoft 365 services [1].
Malicious actors typically gain entry to organizations’ Microsoft 365 environments by abusing either stolen account credentials or stolen session cookies [2]. Once inside, actors can access sensitive data within mailboxes or SharePoint repositories, and send out emails or Teams messages. This activity can often result in serious financial harm, especially in cases where the malicious actor’s end-goal is to elicit fraudulent transactions.
Darktrace regularly observes malicious actors behaving in predictable ways once they gain access to customer Microsoft 365 environment. One typical example is the creation of new inbox rules and sending deceitful emails intended to convince recipients to carry out subsequent actions, such as following a malicious link or providing sensitive information. It is also common for actors to register new applications in Azure AD so that they can be used to conduct follow-up activities, like mass-mailing or data theft. The registration of applications in Azure AD therefore seems to be a relatively predictable threat actor behavior [3][4]. Darktrace DETECT understands that unusual application registrations in Azure AD may constitute a deviation in expected behavior, and therefore a possible indicator of account compromise.
These registrations of applications in Azure AD are evidenced by creations of, as well as assignments of permissions to, Service Principals in Azure AD. Darktrace has detected a growing trend in actors creating and assigning permissions to a Service Principal named ‘PerfectData Software’. Further investigation of this Azure AD activity revealed it to be part of an ongoing account takeover.
‘PerfectData Software’ Activity
Darktrace observed variations of the following pattern of activity relating to an application named ‘PerfectData Software’ within its customer base:
- Actor signs in to a Microsoft 365 account from an endpoint associated with a Virtual Private Server (VPS) or Virtual Private Network (VPN) service
- Actor registers an application called 'PerfectData Software' with Azure AD, and then grants permissions to the application
- Actor accesses mailbox data and creates inbox rule
In two separate incidents, malicious actors were observed conducting their activities from endpoints associated with VPN services (HideMyAss (HMA) VPN and Surfshark VPN, respectively) and from endpoints within the Autonomous System AS396073 MAJESTIC-HOSTING-01.
In March 2023, Darktrace observed a malicious actor signing in to a Microsoft 365 account from a Kuwait-based IP address within the Autonomous System, AS198605 AVAST Software s.r.o. This IP address is associated with the VPN service, HMA VPN. Over the next couple of days, an actor (likely the same malicious actor) signed in to the account several more times from two different Nigeria-based endpoints, as well as a VPS-related endpoint and a HMA VPN endpoint.
During their login sessions, the actor performed a variety of actions. First, they created and assigned permissions to a Service Principal named ‘PerfectData Software’. This Service Principal creation represents the registration of an application called ‘PerfectData Software’ in Azure AD. Although the reason for registering this application is unclear, within a few days the actor registered and granted permission to another application, ‘Newsletter Software Supermailer’, and created a new inbox rule names ‘s’ on the mailbox of the hijacked account. This inbox rule moved emails meeting certain conditions to a folder named ‘RSS Subscription. The ‘Newsletter Software Supermailer’ application was likely registered by the actor to facilitate mass-mailing activity.
Immediately after these actions, Darktrace detected the actor sending out thousands of malicious emails from the account. The emails included an attachment named ‘Credit Transfer Copy.html’, which contained a suspicious link. Further investigation revealed that the customer’s network had received several fake invoice emails prior to this initial intrusion activity. Additionally, there was an unusually high volume of failed logins to the compromised account around the time of the initial access.

In a separate case also observed by Darktrace in March 2023, a malicious actor was observed signing in to a Microsoft 365 account from an endpoint within the Autonomous System, AS397086 LAYER-HOST-HOUSTON. The endpoint appears to be related to the VPN service, Surfshark VPN. This login was followed by several failed and successful logins from a VPS-related within the Autonomous System, AS396073 MAJESTIC-HOSTING-01. The actor was then seen registering and assigning permissions to an application called ‘PerfectData Software’. As with the previous example, the motives for this registration are unclear. The actor proceeded to log in several more times from a Surfshark VPN endpoint, however, they were not observed carrying out any further suspicious activity.

It was not clear in either of these examples, nor in fact any of cases observed by Darktrace, why actors had registered and assigned permissions to an application called ‘PerfectData Software’, and there do not appear to be any open-source intelligence (OSINT) resources or online literature related to the malicious usage of an application by that name. That said, there are several websites which appear to provide email migration and data recovery/backup tools under the moniker ‘PerfectData Software’.
It is unclear whether the use of ‘PerfectData Software’ by malicious actors observed on the networks of Darktrace customers was one of these tools. However, given the nature of the tools, it is possible that the actors intended to use them to facilitate the exfiltration of email data from compromises mailboxes.
If the legitimate software ‘PerfectData’ is the application in question in these incidents, it is likely being purchased and misused by attackers for malicious purposes. It is also possible the application referenced in the incidents is a spoof of the legitimate ‘PerfectData’ software designed to masquerade a malicious application as legitimate.
Darktrace Coverage
Cases of ‘PerfectData Software’ activity chains detected by Darktrace typically began with an actor signing into an internal user’s Microsoft 365 account from a VPN or VPS-related endpoint. These login events, along with the suspicious email and/or brute-force activity which preceded them, caused the following DETECT models to breach:
- SaaS / Access / Unusual External Source for SaaS Credential Use
- SaaS / Access / Suspicious Login Attempt
- SaaS / Compromise / Login From Rare Following Suspicious Login Attempt(s)
- SaaS / Email Nexus / Unusual Location for SaaS and Email Activity
Subsequent activities, including inbox rule creations, registration of applications in Azure AD, and mass-mailing activity, resulted in breaches of the following DETECT models.
- SaaS / Admin / OAuth Permission Grant
- SaaS / Compromise / Unusual Logic Following OAuth Grant
- SaaS / Admin / New Application Service Principal
- IaaS / Admin / Azure Application Administration Activities
- SaaS / Compliance / New Email Rule
- SaaS / Compromise / Unusual Login and New Email Rule
- SaaS / Email Nexus / Suspicious Internal Exchange Activity
- SaaS / Email Nexus / Possible Outbound Email Spam
- SaaS / Compromise / Unusual Login and Outbound Email Spam
- SaaS / Compromise / Suspicious Login and Suspicious Outbound Email(s)

In cases where Darktrace RESPOND™ was enabled in autonomous response mode, ‘PerfectData Software’ activity chains resulted in breaches of the following RESPOND models:
• Antigena / SaaS / Antigena Suspicious SaaS Activity Block
• Antigena / SaaS / Antigena Significant Compliance Activity Block
In response to these model breaches, Darktrace RESPOND took immediate action, performing aggressive, inhibitive actions, such as forcing the actor to log out of the SaaS platform, and disabling the user entirely. When applied autonomously, these RESPOND actions would seriously impede an attacker’s progress and minimize network disruption.

In addition, Darktrace Cyber AI Analyst was able to autonomously investigate registrations of the ‘PerfectData Software’ application and summarized its findings into digestible reports.

Conclusion
Due to the widespread adoption of Microsoft 365 services in the workplace and continued emphasis on a remote workforce, account hijackings now pose a more serious threat to organizations around the world than ever before. The cases discussed here illustrate the tendency of malicious actors to conduct their activities from endpoints associated with VPN services, while also registering new applications, like PerfectData Software, with malicious intent.
While it was unclear exactly why the malicious actors were using ‘PerfectData Software’ as part of their account hijacking, it is clear that either the legitimate or spoofed version of the application is becoming an very likely emergent piece of threat actor tradecraft.
Darktrace DETECT’s anomaly-based approach to threat detection allowed it to recognize that the use of ‘PerfectData Software’ represented a deviation in the SaaS user’s expected behavior. While Darktrace RESPOND, when enabled in autonomous response mode, was able to quickly take preventative action against threat actors, blocking the potential use of the application for data exfiltration or other nefarious purposes.
Appendices
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
Reconnaissance:
• T1598 – Phishing for Information
Credential Access:
• T1110 – Brute Force
Initial Access:
• T1078.004 – Valid Accounts: Cloud Accounts
Command and Control:
• T1105 – Ingress Tool Transfer
Persistence:
• T1098.003 – Account Manipulation: Additional Cloud Roles
Collection:
• T1114 – Email Collection
Defense Evasion:
• T1564.008 – Hide Artifacts: Email Hiding Rules
Lateral Movement:
• T1534 – Internal Spearphishing
Unusual Source IPs
• 5.62.60[.]202 (AS198605 AVAST Software s.r.o.)
• 160.152.10[.]215 (AS37637 Smile-Nigeria-AS)
• 197.244.250[.]155 (AS37705 TOPNET)
• 169.159.92[.]36 (AS37122 SMILE)
• 45.62.170[.]237 (AS396073 MAJESTIC-HOSTING-01)
• 92.38.180[.]49 (AS202422 G-Core Labs S.A)
• 129.56.36[.]26 (AS327952 AS-NATCOM)
• 92.38.180[.]47 (AS202422 G-Core Labs S.A.)
• 107.179.20[.]214 (AS397086 LAYER-HOST-HOUSTON)
• 45.62.170[.]31 (AS396073 MAJESTIC-HOSTING-01)
References
[1] https://www.investing.com/academy/statistics/microsoft-facts/
[2] https://intel471.com/blog/countering-the-problem-of-credential-theft
[3] https://darktrace.com/blog/business-email-compromise-to-mass-phishing-campaign-attack-analysis
[4] https://darktrace.com/blog/breakdown-of-a-multi-account-compromise-within-office-365
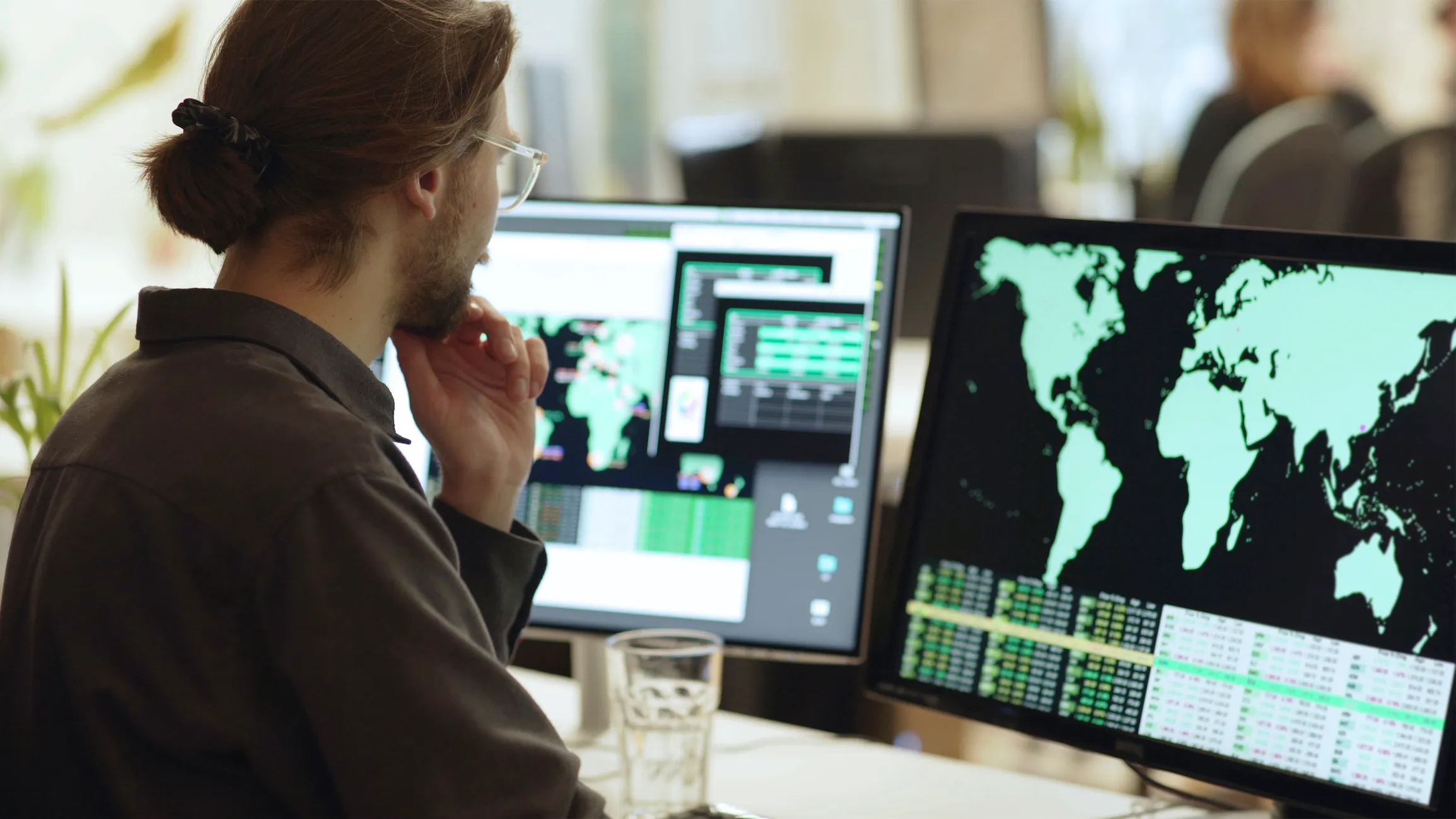































![Cyber AI Analyst Incident Log showing the offending device making over 1,000 connections to the suspicious hostname “zohoservice[.]net” over port 8383, within a specific period.](https://assets-global.website-files.com/626ff4d25aca2edf4325ff97/662971c1cf09890fd46729a1_Screenshot%202024-04-24%20at%201.55.10%20PM.png)